guiding questions

Guiding Questions: A Comprehensive Overview (Updated February 15, 2026)
Guiding questions foster deeper learning, shifting from rote memorization to genuine understanding, like imagining life on a Viking longship.
These inquiries encourage exploration and application, such as role-playing in an Italian café, surpassing simple vocabulary recall exercises.
What are Guiding Questions?
Guiding questions represent a pedagogical shift, moving away from traditional direct instruction towards a more student-centered, inquiry-based learning approach. They aren’t simply questions seeking a single, correct answer; instead, they are carefully crafted prompts designed to stimulate thought, encourage exploration, and facilitate a deeper understanding of a subject.
Unlike questions that test recall – like asking students to remember facts about Vikings – guiding questions invite students to consider scenarios, such as imagining life aboard a Viking longship. This fosters a more profound and lasting comprehension. They are tools to unlock existing knowledge and build new connections, prompting students to actively construct their own meaning.
Effective guiding questions often lack a clear “right” answer, encouraging diverse perspectives and promoting critical thinking. They are the cornerstone of active learning, transforming students from passive recipients of information into active participants in their own educational journey.
The Core Principle: Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning, at its heart, champions student curiosity and active investigation. Guiding questions are the engine driving this process, shifting the focus from teacher-led delivery to student-driven discovery. Instead of being told information, students are guided to uncover it themselves through thoughtful questioning and exploration.
This approach mirrors real-world problem-solving, where definitive answers aren’t always readily available. Students learn to formulate their own questions, analyze information, and draw conclusions – skills crucial for success beyond the classroom. The power lies in prompting students to ask “what if?” and “why?” rather than simply “what?”
By embracing inquiry, educators cultivate a learning environment where mistakes are seen as opportunities for growth and where students feel empowered to take ownership of their learning journey, fueled by carefully constructed guiding questions.
Why Use Guiding Questions Instead of Direct Instruction?
Direct instruction, while efficient for conveying information, often results in passive learning and limited retention. Guiding questions, conversely, actively engage students, fostering deeper understanding and long-term memory. Simply remembering facts about Vikings pales in comparison to considering their daily lives – a question-driven approach.
Traditional methods prioritize knowing; guiding questions prioritize understanding. They move beyond surface-level recall, prompting students to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information. This cultivates critical thinking skills, preparing them for complex challenges.
Furthermore, guiding questions address the common issue of “jumbled word-salad” – half-remembered phrases – by encouraging practical application, like ordering coffee in Italian, solidifying language acquisition through genuine use.

Benefits of Implementing Guiding Questions
Guiding questions unlock deeper comprehension, boost critical thinking, and ignite student engagement, transforming classrooms into vibrant, student-centered learning environments.
Deeper Understanding & Retention
Guiding questions move beyond superficial memorization, fostering a profound and lasting grasp of concepts. Instead of simply recalling facts – like ten details about Vikings – students actively construct knowledge through inquiry. This approach encourages them to consider complex scenarios, such as visualizing life aboard a Viking longship, leading to a richer, more nuanced understanding.
When students grapple with questions that demand thoughtful responses, information isn’t passively received; it’s actively processed and integrated into existing knowledge frameworks. This active engagement significantly improves retention rates. The process of formulating answers, even tentative ones, solidifies learning in a way that rote memorization simply cannot achieve. It’s about building understanding, not just accumulating facts.

Promoting Critical Thinking Skills
Guiding questions are instrumental in cultivating critical thinking, moving students beyond simple recall towards analysis, evaluation, and creation. They challenge assumptions and encourage students to justify their reasoning, rather than accepting information at face value. For example, instead of merely stating what happened in a historical event, students are prompted to analyze why it happened and its broader implications.
Probing questions, like “What makes you say that?” or “Could you rephrase that?” force students to articulate their thought processes, identify gaps in their understanding, and refine their arguments. This iterative process of questioning, responding, and revising is at the heart of critical thinking. It empowers students to become independent, discerning thinkers capable of navigating complex information and forming well-supported conclusions.
Increased Student Engagement & Participation
Guiding questions dramatically boost student engagement by transforming the classroom from a passive listening environment to an active learning space. When students are asked to explore, hypothesize, and share their perspectives, they become invested in the learning process. This active participation fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility for their own understanding.
Encouraging peer-to-peer responses, where students build upon each other’s ideas, further amplifies engagement. Allowing sufficient response time and embracing “awkward silences” signals that all contributions are valued, even those that require thoughtful consideration; By connecting student responses to the broader topic, educators demonstrate the relevance of their input, increasing motivation and participation levels across the board.
Fostering a Student-Centered Classroom
Guiding questions are instrumental in shifting the focus from teacher-led instruction to a truly student-centered learning environment. Instead of simply delivering information, educators become facilitators, guiding students to construct their own knowledge through inquiry and exploration. This approach empowers students to take ownership of their learning journey, fostering independence and self-reliance.
By responding to incorrect answers with further probing questions – “What makes you say that?” or “Could you rephrase that?” – teachers validate student thinking and encourage deeper analysis. This creates a safe space for risk-taking and intellectual curiosity, where students feel comfortable sharing their ideas, even if imperfect. Ultimately, guiding questions cultivate a classroom where learning is driven by student interests and questions.

Types of Guiding Questions
Guiding questions encompass open-ended inquiries, probing follow-ups, hypothetical scenarios, and clarifying requests—each designed to stimulate thought and deepen comprehension effectively.
Open-Ended Questions: Encouraging Exploration
Open-ended questions are the cornerstone of inquiry-based learning, deliberately avoiding simple “yes” or “no” answers. They invite students to elaborate, providing detailed responses that reveal their current understanding and thought processes. These questions begin with phrases like “What if…”, “How does…”, or “Why do you think…?” prompting expansive thinking.
Unlike direct questions demanding specific recall, open-ended prompts encourage students to explore concepts from multiple angles, fostering a sense of ownership over their learning. For instance, instead of asking “Did Vikings raid villages?”, a teacher might ask, “What would life be like aboard a Viking longship?” This encourages imaginative engagement and a more nuanced understanding of Viking culture.
The beauty of these questions lies in their ability to uncover unexpected insights and reveal the depth of student knowledge, going beyond surface-level comprehension.
Probing Questions: Digging Deeper into Responses
Probing questions build upon initial student responses, acting as a follow-up to encourage further elaboration and critical analysis. They aren’t about finding the “right” answer, but rather understanding the reasoning behind a student’s thought process. Phrases like “What makes you say that?” or “Could you rephrase that?” are invaluable tools.
When a student offers an incomplete or unclear answer, resisting the urge to correct them directly is crucial. Instead, a probing question gently guides them to refine their thinking and articulate their ideas more precisely. This technique transforms potential errors into learning opportunities, fostering self-reflection and deeper comprehension.
Effective probing doesn’t feel like an interrogation; it’s a supportive dialogue designed to unlock a student’s full potential and reveal the nuances of their understanding.
Hypothetical Questions: Stimulating Imagination

Hypothetical questions propel students beyond the confines of established facts, encouraging them to explore possibilities and engage their imaginations. These “what if” scenarios aren’t about predicting the future, but about applying existing knowledge in novel contexts. Consider asking, “What if the Vikings had never discovered North America?”
This type of inquiry fosters creative problem-solving and encourages students to consider multiple perspectives. It allows them to grapple with complex concepts in a low-stakes environment, free from the pressure of finding a definitive answer. The focus shifts from recall to application and analysis.
By prompting students to envision alternative realities, hypothetical questions cultivate intellectual curiosity and a willingness to think outside the box.
Clarifying Questions: Ensuring Comprehension
Clarifying questions are essential for verifying student understanding and addressing potential misconceptions. Rather than simply accepting an initial response, these questions gently probe for deeper clarity. Instead of dismissing an unclear answer, respond with phrases like, “Could you rephrase that?” or “What makes you say that?”
This approach isn’t about finding fault, but about supporting students in articulating their thoughts more precisely. It encourages them to reflect on their reasoning and identify any gaps in their understanding.
Effective clarifying questions create a safe space for students to admit confusion and seek assistance, fostering a more collaborative learning environment. They ensure everyone is on the same page before moving forward.

Effective Techniques for Using Guiding Questions
Employ patience; allow ample response time and embrace pauses. Encourage peer interaction and connect answers to the core topic for enhanced engagement.
Allowing Sufficient Response Time
A crucial technique when utilizing guiding questions is providing students with adequate time to formulate thoughtful responses. Resist the urge to immediately fill silences; these pauses are often productive spaces where deeper cognitive processing occurs. Students require moments to retrieve information, connect concepts, and articulate their ideas effectively.
Rushing the process can lead to superficial answers and hinder the development of critical thinking skills. Encourage students to elaborate on their initial thoughts, and be patient as they navigate complex ideas. This deliberate pacing fosters a more inclusive learning environment, allowing all students, regardless of their processing speed, to participate meaningfully. Remember, the goal isn’t rapid-fire answers, but substantial understanding.
Embracing “Awkward Silences”
Resist the instinct to immediately jump in and fill pauses following a guiding question. These “awkward silences” are not voids of learning, but rather vital spaces where students are actively engaging in cognitive work. They are processing information, constructing responses, and grappling with complex ideas – all essential components of deep understanding.
As educators, we must learn to be comfortable with these moments of quiet contemplation. Prematurely offering answers or rephrasing the question robs students of the opportunity to independently arrive at their own conclusions. Allowing sufficient wait time demonstrates respect for their thinking process and encourages more thoughtful, elaborate responses. Embrace the silence; it’s a sign of active minds at work.
Responding to Incorrect Answers with Further Questions
Instead of simply correcting a student’s inaccurate response to a guiding question, view it as a valuable opportunity for deeper exploration. Avoid declarative statements of “right” or “wrong.” Instead, respond with probing follow-up questions designed to uncover the student’s reasoning and thought process.
Phrases like “That’s interesting. What makes you say that?” or “Could you rephrase that?” encourage students to articulate their thinking and identify potential gaps in their understanding. This approach fosters a safe learning environment where mistakes are seen not as failures, but as stepping stones towards clarity. It also allows you to diagnose misconceptions and tailor your guidance accordingly, promoting genuine learning and critical thinking.
Encouraging Peer-to-Peer Responses
A powerful extension of the guiding questions technique involves directing students to respond to each other’s ideas. After a student offers an answer, instead of immediately providing feedback yourself, ask the class, “What do others think about that response?” or “Does anyone agree or disagree, and why?”
This fosters a collaborative learning environment where students actively listen, analyze, and build upon each other’s contributions. It shifts the responsibility for learning from the teacher to the students themselves, promoting deeper engagement and understanding. Peer interaction also allows students to articulate their thinking in different ways, solidifying their own comprehension and benefiting from diverse perspectives.
Connecting Student Responses to the Broader Topic
To maximize the impact of guiding questions, consistently link student answers back to the overarching themes and objectives of the lesson. After a student shares their thoughts, explicitly state how their response relates to the larger context. For example, you might say, “That’s a great point, and it connects directly to our discussion about…” or “How does this idea help us understand the main concept of…?”
This technique reinforces the relevance of individual contributions and demonstrates how each piece of information contributes to a more complete understanding. It also helps students see the interconnectedness of ideas, fostering a more holistic and meaningful learning experience. By framing responses within the broader topic, you increase interaction and participation.

Guiding Questions in Different Educational Contexts
Across disciplines – history, languages, science, and math – guiding questions move beyond simple recall, promoting practical application and conceptual understanding for students.
History Education: Beyond Memorization
In history, guiding questions transcend the limitations of simply memorizing dates and names. Instead of asking students to recall ten facts about Vikings, a more impactful approach involves posing questions that stimulate imagination and critical thinking. For example, “What would life actually be like aboard a Viking longship?” compels students to consider the practicalities, challenges, and daily experiences of those historical figures.
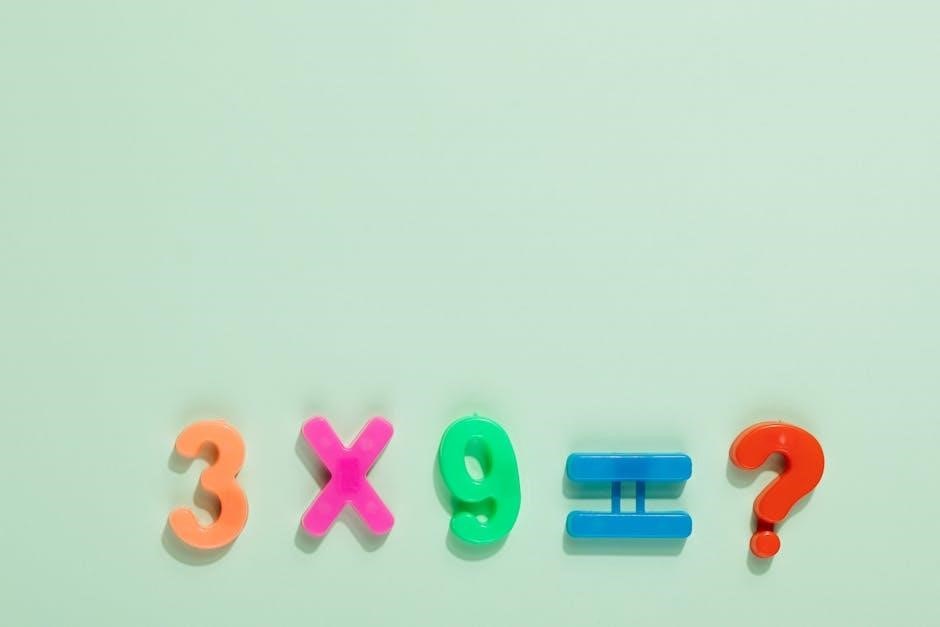
This inquiry-based method fosters a deeper, more nuanced understanding of the past. Students aren’t just passively receiving information; they are actively constructing knowledge by grappling with complex scenarios and considering multiple perspectives. Guiding questions encourage students to analyze historical events, interpret primary sources, and draw their own informed conclusions, moving beyond superficial memorization towards genuine historical comprehension.
Language Learning: Practical Application
Guiding questions revolutionize language acquisition by prioritizing practical application over rote memorization of vocabulary lists. Rather than simply asking students to name three beverages in Italian and use them in a sentence – often resulting in “jumbled word-salad” – pose a scenario: “You are a customer in an Italian café. How would you order a coffee?”
This immersive approach forces students to actively utilize the language in a realistic context, fostering fluency and confidence. Role-playing and similar activities encourage spontaneous communication and problem-solving, solidifying understanding far more effectively than traditional drills. Guiding questions bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world usage, accelerating language mastery and promoting genuine communicative competence.
Science Education: Fostering Scientific Inquiry
Guiding questions are pivotal in transforming science education from a passive reception of facts to an active process of scientific inquiry. Instead of directly providing answers, educators can pose questions that stimulate investigation and critical thinking. For example, rather than stating the properties of a specific chemical reaction, ask: “What observations lead you to believe a chemical change has occurred?”
This approach encourages students to formulate hypotheses, design experiments, analyze data, and draw conclusions – mirroring the work of real scientists. By prompting students to explain why they believe something, guiding questions cultivate a deeper understanding of scientific principles and the scientific method itself, fostering a lifelong curiosity and analytical skillset.
Mathematics Education: Conceptual Understanding
Guiding questions revolutionize mathematics education by prioritizing conceptual understanding over rote memorization of procedures. Instead of simply asking students to solve for ‘x’, a guiding question might be: “Can you explain, in your own words, why we perform the same operation on both sides of the equation?” This shifts the focus from getting the right answer to understanding the underlying mathematical principles.
Such inquiries encourage students to articulate their reasoning, identify patterns, and make connections between different mathematical concepts. This approach fosters a more robust and flexible understanding, enabling students to apply their knowledge to novel problems and develop a genuine appreciation for the beauty and logic of mathematics, rather than just following algorithms.

Potential Challenges & Solutions
Addressing hesitation requires patience; embrace silences, encourage all responses, and rephrase questions for clarity, fostering a safe learning environment for all students.
Students’ Hesitation to Participate
A common hurdle when implementing guiding questions is student reluctance to contribute. This hesitation often stems from fear of incorrect answers or a general discomfort with open-ended inquiry. Creating a psychologically safe classroom is paramount; students need to believe it’s okay to be wrong.
Allowing sufficient response time is crucial. Rushing students can exacerbate anxiety. Embrace those “awkward silences” – they signal thinking is happening! Reassure students that there are no “right” or “wrong” answers initially, but rather opportunities to explore ideas.
Frame questions carefully, avoiding language that implies judgment. Normalize the process of refining thoughts and building upon each other’s contributions. Small group discussions can also lower the stakes, encouraging quieter students to participate before sharing with the whole class.
Managing Diverse Responses
Guiding questions inevitably elicit a wide range of responses, demanding skillful facilitation. Expect answers that are tangential, incomplete, or even seemingly off-topic. The key isn’t to immediately correct, but to build upon these contributions.
Acknowledge all responses as valid starting points. Use probing questions – “That’s interesting, what makes you say that?” or “Could you rephrase that?” – to encourage elaboration and deeper thinking. This demonstrates respect and encourages further exploration.
Connect student responses to the broader topic framework, highlighting relevance and fostering interaction. Use one student’s answer as a springboard for further discussion, linking it to core concepts. This demonstrates the value of diverse perspectives and builds a cohesive understanding.
Avoiding Leading Questions
Guiding questions should stimulate independent thought, not steer students toward a predetermined answer. Leading questions subtly suggest the “right” response, undermining the inquiry-based learning process. For example, instead of asking “Wasn’t the Viking longship a remarkably efficient design?”, pose “What advantages might the longship’s design have offered?”
Focus on open-ended phrasing that encourages exploration. Avoid questions containing qualifiers or assumptions. The goal is to uncover student reasoning, not to confirm existing knowledge.
Self-reflection is crucial. Before posing a question, consider if it subtly implies a desired outcome. Reword it to be neutral and genuinely inquisitive, fostering authentic student engagement and critical thinking.
Assessing the Effectiveness of Guiding Questions
Evaluating the impact of guiding questions extends beyond simply checking for correct answers. Observe student engagement – are they actively participating and responding to each other? Are responses thoughtful and demonstrate deeper understanding, moving beyond surface-level recall?
Analyze the quality of discussion. Do students build upon each other’s ideas, demonstrating critical thinking? Are they comfortable with “awkward silences” as they formulate responses, indicating genuine processing?
Consider formative assessment techniques like quick writes or exit tickets to gauge comprehension. Adjust future questions based on observed student responses and areas needing clarification, refining your approach for optimal learning.










































































